Setting Up a Company in Saudi Arabia: An Overview and Key Notes
Introduction
In a global landscape ripe with opportunity, Saudi Arabia stands as a beacon of promise, offering significant potential for business growth and expansion. Central to this transformation is the Vision 2030 program, a strategic initiative aimed at diversifying the nation’s economy and reducing its dependence on oil. This vision seeks to create a more dynamic and sustainable economic environment, opening the door for international and foreign companies to establish and grow their presence in the Kingdom.
Establishing a business in Saudi Arabia requires a thorough understanding of the regulatory framework and the various administrative procedures involved. This guide provides an overview of the main phases and key considerations for setting up a company in Saudi Arabia, particularly for international and foreign investors.
Main Phases of Company Setup
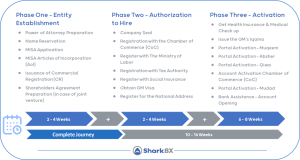
Key Notes of the Setup Journey
Before registering a foreign-owned company, obtaining pre-approval from the Ministry of Investment of Saudi Arabia (MISA) is mandatory. This regulatory authority reviews the foreign investment plan and documentation before issuing the license. After approval, the company incorporation application can proceed, including the preparation of necessary resolutions, documentation, and the drafting of a shareholder’s agreement to protect the partners’ interests. Following this, the commercial registration certificate is obtained.
The government subscription fee for MISA portal services is SAR 12,000 in the first year and SAR 60,000 each year thereafter. Additionally, a lease agreement for physical office premises is required to issue the Municipality License. Various workspace solutions and other necessities like a national address, PO Box, and local phone number are essential.
Appointing a General Manager with a local visa is necessary. For expatriate employees, securing a local work permit (iqama) immediately after company registration is crucial as the approval process may take up to two months.
Compliance with Saudi Arabian law requires each entity to register with the Ministry of Labor (MHRSD), the General Organization for Social Insurance (GOSI), and the Zakat, Tax and Customs Authority (ZATCA) for corporation tax and VAT. Completing all statutory registrations and activating the online portals accounts are essential steps. Maintaining separate financial records and a local business bank account is crucial for compliance, transparency, tax obligations, and overall legal adherence.
Ongoing support for bookkeeping, monthly and quarterly government reporting, and employee matters may be needed. Maintaining regulatory compliance is crucial for any business operating in Saudi Arabia to avoid legal issues. Companies need to maintain financial reporting, tax compliance, corporate governance, employment compliance, and various other regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Setting up a company in Saudi Arabia offers significant potential but requires a strategic approach and thorough understanding of the local business landscape. Understanding the phases and key requirements involved can help ensure a seamless and successful business setup. For more detailed guidance and support, visit our website or contact us for a free consultation.
